Here's a list over simple fixes and tasks in Debian that I've been running into the past few weeks. I'll be adding to it over time.
Index of the ever-growing list
1. INIT: Id "co" respawning too fast: disabled for 5 minutes
2. Boot into terminal instead of gdm (kdm/xdm etc.)
3. Change the logical name of an ethernet card -- why do I have
eth1 and
rename2 and how to get eth0 and eth1 instead?
4. Configuring ethernet cards in gnome3/gnome-shell -- can't save changes in network-manager
5. Gnome3/gnome-shell -- Alt+f2 yields "command not found"
6. /etc/hosts keep on being overwritten
7. Getting Leadtek DTV1000s to work in Linux
8. Turning off terminal beep
9. Trouble with apt-get -- can't do apt-get update
10. Adding and removing pages in a pdf using pdftk
11. Updating the locate database
12. My gateway doesn't play well with sinfo
13. Basic proxy via ssh
14. Using a Compose key to type non-standard characters like å, ä, ö
15. Command not found, did you mean ..? Installing command-not-found
16. apt-listbugs
17. Thunar is the default file manager in spite of me running Gnome!
18. Nautilus recognises compressed files, but doesn't know how to open them
19. Finding out when a package was installed
20. Showing your kernel and debian version
21. Screen dump in the terminal
22. Enable java in chrome
23. Changing element colour in gdis
24. CCSD mercury /lib/libc6.so
25. Daemons...rcconf, sysv-rc-conf and update-rc.d
26. Adjusting your webcam
27. Command line burning of iso
29. USB support in virtualbox
30. Start-up applications in Gnome 3.4
31. Changing pulseaudio volume from the command line
1. INIT: Id "co" respawning too fast: disabled for 5 minutes
References:
http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/fedora-35/init-id-co-respawning-too-fast-disabled-for-5-minutes-736393/ and
http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-newbie-8/reload-inittab-without-reboot-366505/
Instructions:
Edit /etc/inittab
Find a line saying
co:2345:respawn:/sbin/getty hvc0 9600 linux
and comment it out by prefixing it with a #;
#co:2345:respawn:/sbin/getty hvc0 9600 linux
Run
sudo init q
to make the changes take effect.
2. Boot into terminal instead of gdm (kdm/xdm etc.)
Instructions:
Method 1:
Edit /etc/default/grub
Change
GRUB_CMDLINE_DEFAULT="quiet splash nomodeset nouveau.modeset=0"
to
GRUB_CMDLINE_DEFAULT="quiet splash text nomodeset nouveau.modeset=0"
(You may obviously not have nomodset etc. in that line. )
IMPORTANT: run
sudo update-grub
to make the changes take effect.
To start up a desktop type startx
3. Change the logical name of an ethernet card -- why do I have eth1 and rename2 and how to get eth0 and eth1 instead?
Edit /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
You'll find lines like this one:
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="08:00:27:e9:90:00", ATTR{dev_id}=="0x0", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="eth0"
You can bind a logical name (NAME="eth0") to a mac address (ATTR{address}=="") here.
NOTE that interfaces handled by network-manager won't show up here. Unless you initialise a network interface in /etc/network/interfaces they will be handled by network-manager.
4. Configuring ethernet cards in gnome3/gnome-shell -- can't save changes in network-manager
If you click on the network icon in gnome3/gnome-shell, then network settings, wired, configure and edit the connection, then hit save, you may find that it won't save the changes. You may even see a black box asking for admin password flash by and disappearing.
There's no real fix -- make sure to start the Network Connections application the 'normal' way instead (top left corner, type in networ... and pick network connections. You'll be able to save your changes now.
5. Gnome3/gnome-shell -- Alt+f2 yields "command not found"
Edit /usr/share/gnome-shell/js/misc/util.js
Delete all instances of argc e.g. if it say
success, argc, argv -- change to
success, argv
6. /etc/hosts keep on being overwritten
The culprit is -- no surprise --- network-manager. You can either fight it, or use network-manager to manage your configuration.
My particular case was this: my computer is called tantalum. I don't want tantalum to be associated with 127.0.1.1 or 127.0.0.1 though (mpich2 reasons), but want to associate the host name with the external ip address (192.168.1.102). This is a typical case where you'd edit /etc/hosts and you'd be done. Apart from the fact that the file gets overwritten on each boot.
To force it using network manager, start network-admin in the terminal or using alt+f2, go to Hosts, and remove your hostname from 127.0.1.1 and add it using the desired ip address.
Reading
this it seems like it's possible making changes in the configuration files directly. In particular, the option to define unmanaged devices looks interesting.
Network Manager is one of those programs which are great when you need basic functionality from your system, but an absolute pain in the arse when you need to do something non-standard.
7. Getting Leadtek DTV1000s to work in Linux
This is a bit of a non-fix...the card should work out of the box, so to speak.
However, it didn't for me.
If lspci gives Philips something or other and rev ff rather than e.g. rev 01 as well as MMIO errors, check your BIOS! I kept on getting very little information about my card when doing lspci -vn and it turned out that I had disabled PnP in the BIOS. Once the bios was set to allow the OS to configure PCI devices (Plug-and-play OS), everything worked like a charm.
I put
options saa7134 tuner=48 card=175
in my /etc/modules, but I'm not sure this matters.
Long before discovering that I built and installed the v4l-dvb media build from the git repos,
(Easily done like this:
git clone git://linuxtv.org/media_build.git
cd media_build
./build
)
and downloaded the firmware packages by Mike Krufky (
http://tw1965.myweb.hinet.net/), and spent time reading forum posts (starting with
http://forums.whirlpool.net.au/archive/942269). What I'm saying is that I don't THINK you will need to install or compile anything, but you MAY have to. Make sure your BIOS settings are right first though.
Here's
lcpci -vvnn for a working leadtek dtv1000s:
01:06.0 Multimedia controller [0480]: Philips Semiconductors SAA7130 Video Broadcast Decoder [1131:7130] (rev 01)
Subsystem: LeadTek Research Inc. WinFast DTV1000S [107d:6655]
Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx-
Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B+ ParErr- DEVSEL=medium >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-
Latency: 64 (21000ns min, 8000ns max)
Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 19
Region 0: Memory at deeffc00 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=1K]
Capabilities: <access denied>l
Kernel driver in use: saa7134
Here's dmesg|grep saa
7.213108] saa7130/34: v4l2 driver version 0, 2, 17 loaded
[ 7.213383] saa7134 0000:01:06.0: PCI INT A -> Link[LNKC] -> GSI 19 (level, low) -> IRQ 19
[ 7.213387] saa7130[0]: found at 0000:01:06.0, rev: 1, irq: 19, latency: 64, mmio: 0xdeeffc00
[ 7.213392] saa7130[0]: subsystem: 107d:6655, board: Leadtek Winfast DTV1000S [card=175,autodetected]
[ 7.213407] saa7130[0]: board init: gpio is 2020000
[ 7.260128] input: saa7134 IR (Leadtek Winfast DTV as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:04.0/0000:01:06.0/rc/rc0/input6
[ 7.260181] rc0: saa7134 IR (Leadtek Winfast DTV as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:04.0/0000:01:06.0/rc/rc0
[ 7.412048] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 00: 7d 10 55 66 54 20 1c 00 43 43 a9 1c 55 d2 b2 92
[ 7.412055] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 10: 00 ff 82 0e ff 20 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412060] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 20: 01 40 01 01 01 ff 01 03 08 ff 00 8a ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412065] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 30: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412070] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 40: ff 35 00 c0 00 10 03 02 ff 04 ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412074] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 50: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412079] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 60: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412084] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 70: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412089] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 80: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412093] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom 90: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412098] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom a0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412103] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom b0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412108] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom c0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412113] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom d0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412117] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom e0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.412122] saa7130[0]: i2c eeprom f0: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
[ 7.608255] saa7130[0]: registered device video0 [v4l2]
[ 7.608280] saa7130[0]: registered device vbi0
8. Turning off terminal beep
To remove immediately:
sudo modprobe -r pcspkr snd_pcsp
To turn off permanently:
create a file called
blacklist.conf in
/etc/modprobe.d
Put the following in it:
blacklist pcspkr
blacklist snd_pcsp
9. Trouble with apt-get -- can't do apt-get update
The issue:
On running
sudo apt-get update
you get
Reading package lists... Error!
E: Encountered a section with no Package: header
E: Problem with MergeList /var/lib/apt/lists/192.168.1.1:3142_ftp.au.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_contrib_i18n_Translation-en
E: The package lists or status file could not be parsed or opened.
The solution:
First, look in /var/lib/apt/lists
ls /var/lib/apt/lists/ -lah | grep contrib |grep i18n| grep testing
which gives
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 34K Feb 3 07:01 192.168.1.1:3142_ftp.au.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_contrib_i18n_Translation-en
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 121K Feb 3 07:01 192.168.1.1:3142_ftp.au.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_contrib_i18n_Translation-en%5fAU
Then remove the offending file:
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/192.168.1.1:3142_ftp.au.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_contrib_i18n_Translation-en
And do sudo apt-get update again -- it should now work.
If it doesn't then you're lacking bzip2 and should look at this post.
10. Adding and removing pages in a pdf using pdftk
Scenario:
I have a pdf document which I need to sign on the last page. Instead of printing the entire document and scanning it, I print the last page, scan it and replace the last page of the original pdf with it.
How to do:
In my case I have a 27 page document and want to replace pages 25, 26 and 27..
Remove pages 25-27 from original document i.e.keep 1-24:
pdftk original.pdf cat 1-24 output new.pdf
Add new pages 25,26 and 27 which make up signatures.pdf
pdftk cat new.pdf signatures.pdf output final_document
11. Updating the locate database
locate is a good command for finding certain types of files. It seems to be continously, but not immediately, updated.
To force the locate database to update:
sudo updatedb
12. My gateway doesn't play well with sinfo
My gateway is a computer with two eth cards -- one connected to the internet and one to a switch making up a local subnet. All the boxes on the local subnet can see each other's sinfod instances, but not the gateway machine.
Turns out the fix is simple -- change
/etc/default/sinfo:
from
#OPTS="${OPTS} --bcastaddress=127.0.0.1"
to
OPTS="${OPTS} --bcastaddress=192.168.1.255"
which is the appropriate broadcast for my subnet.
Sinfo is cool and a 'must' for anyone running a small LAN for computational reasons:
/ 3 nodes, 11 CPUs total CPU utilization: 2.7% ( 0.351 GHz / 12.800 GHz )
beryllium uuuuuusssiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii-------------------------( 4) mem: 55.6% swap: 0.0% us: 4.8% id: 92.7% me S 8.9 0 chrome
me S 6.6 0 vmd_LINUXAMD64
me S 5.5 0 chrome
me S 4.5 0 gnome-shell
root R 4.0 0 Xorg
kookaburra iiii---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------( 1) mem: 22.9% swap: 0.0% us: 0.0% sy: 0.0% ni: 0.0% wa: 0.0% id:100.0%
me S 0.2 0 sinfo
daemon R 0.1 10 sinfod
ntp S 0.0 0 ntpd
root S 0.0 0 rsyslogd
root S 0.0 0 /usr/sbin/apachtantalum iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii( 1) mem: 20.9% swap: 0.0% us: 0.0% sy: 0.0% ni: 0.0% wa: 0.0% ;id:100.0%
me S 0.3 0 conky
root S 0.2 0 Xorg
me S 0.1 0 gnome-shell
me S 0.1 0 dropbox
me S 0.0 0 linphone-3
If you can't see all the boxes on your gateway, change all the LAN boxes to broadcast on 192.168.1.255 (or the appropriate replacement).
13. Basic proxy via ssh
If you have an ssh account on another server you can use it as a proxy
ssh -C -D 9889 me@remote.server.org
-C turns on compression
-D redirects traffic sent to port 9889 to the remote.server.org
Chrome/Chromium use the system settings for the network connection:
To use the proxy for web browsing on gnome 3/gnome-shell, left-click on the connection icon in the top right corner of your desktop (or just go to System Settings), select Network Settings, Click on the tab called Network Proxy, Method: Manual, and set SOCKS host to localhost and port to 9889. You can also change it in Chrome/Chromium -- preferences/proxy which opens the system-wide network settings.
Iceweasel/Firefox by default uses it's own settings:
Edit/Preferences/Network tab/Connections - Settings... -- Select Manual Proxy Configuration, SOCKS hosts: localhost, port 9889.
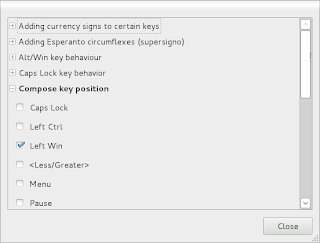
14. Using a Compose key to type non-standard characters like å, ä, ö
In gnome 3/gnome-shell, open Region and Languages in the System Settings; select the Layout tab. Pick your usual language (e.g. English (US)) and click on options. Expand the Compose Key Position and pick a key to use as the Compose Key, e.g. right alt or the windows symbol key.
Now you can type fancy European characters with a lot more ease -- for a list over key sequences, look
here.
Two example -- to type É first touch the compose key (don't hold it down), then ', then shift+E. For å do compose, o, a. For € do compose, =, c. For ö, do compose, ", o.
15. Command not found, did you mean ..? Installing command-not-found
On a basic install of debian, typing nfs gets you
me@lithium:~$ nfs
-bash: nfs: command not found
Linux can do better than that:
Install command-not-found
sudo apt-get install command-not-found
sudo update-command-not-found
Restart the shell (or log in and out)
Now, when typing nfs you get:
me@lithium:~$ nfs
No command 'nfs' found, did you mean:
Command 'lfs' from package 'lustre-utils' (main)
Command 'xfs' from package 'xfs' (main)
Command 'knfs' from package 'openafs-client' (main)
Command 'nns' from package 'tcllib' (main)
Command 'ns' from package 'ns2' (main)
Command 'fs' from package 'openafs-client' (main)
Command 'zfs' from package 'zfs-fuse' (main)
Command 'hfs' from package 'hfsutils-tcltk' (main)
nfs: command not found
16. apt-listbugs
A useful tool for catching problematic packages when you upgrade/dist-upgrade is to use apt-listbugs. It gets invoked automatically when you run sudo apt-get...
Install by
sudo apt-get install apt-listbugs
For an example of it in action, see
http://www.worksinmymind.com/blog/?p=1125
17. Thunar is the default file manager in spite of me running Gnome!
You can either remove thunar -- which you probably got through install xfce4 -- or you can edit .config/xfc4/helpers.rc
me@niobium:~$ cat .config/xfce4/helpers.rc
MailReader=evolution
#FileManager=Thunar
FileManager=nautilus
WebBrowser=google-chrome
18. Nautilus recognises compressed files, but doesn't know how to open them
Install file-roller. You may want to install additional packages as per aptitude show file-roller:
Suggests: arj, binutils, cpio, lha, lzip, lzma, lzop, ncompress, rpm2cpio, rzip, sharutils, unace, unalz, unrar |
p7zip-rar, unzip, xz-utils, zip, zoo
19. Finding out when a package was installed
Look
here.
Listing all packages according to time, most recent last.
ls /var/lib/dpkg/info/*.list -lrth| grep "info/lib"
Looking for a specific subset of packages
ls /var/lib/dpkg/info/*.list -lrth| grep "info/lib"
20. Showing your kernel and debian version
Someone searched for
www.google.co.kr — linux debian version check and ended up on this blog. Well, here are the answers:
me@beryllium:~$ uname -a
Linux beryllium 3.2.0-1-amd64 #1 SMP Sun Feb 5 15:17:15 UTC 2012 x86_64 GNU/Linux
me@beryllium:~$ cat /etc/debian_version
wheezy/sid
21. Screen dump in the terminal
Method 1. Works in the 'true' terminals i.e. ttyX:
If you want to save what is already on the screen into a text file, do
sudo cat /dev/vcsX > screendump.txt
where X is the number of your terminal (e.g. tty
1, tty
2 etc.)
This method does not seem to add linebreaks -- instead it presumes that you're using a standard 80 char terminal.
Method 2. Using framebuffer
First check if you are using the framebuffer
ls /dev/fb0
If so, install fbcat
sudo apt-get install fbcat
Get a screen dump by running
fbgrab screendump.png
22. Enable java in chrome
Java has always been tricky. Sometimes icedtea-plugin has worked, sometimes it hasn't. At the moment it works:
sudo apt-get install icedtea-plugin
update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-6-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/javaws to provide /usr/bin/javaws (javaws) in auto mode.update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-6-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/itweb-settings to provide /usr/bin/itweb-settings (itweb-settings) in auto mode.
Not sure about the java-6-openjdk-amd64 since I actually have openjdk-7 installed and not 6. Try installing openjdk7-7-jdk first.
i A openjdk-6-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT
i A openjdk-6-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (h
i A openjdk-6-jre-lib - OpenJDK Java runtime (architecture indepen
i openjdk-7-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK)
i openjdk-7-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT
i A openjdk-7-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (h
i A openjdk-7-jre-lib - OpenJDK Java runtime (architecture indepent
23. Changing element colour in gdis
GDIS is, in my opinion, the best linux program for generating povray files from crystallographic data. Mainly this is due to the number of different representations which can be selected: from ball-and-stick to polyhedral to surface -- and it allows mixing different representations in the same molecule, which is what sets it apart.
Long story short, in order to change the default element colours you have to manually edit
/usr/share/gdis/gdis.elements
Each element is contained between a
%gdis_elemen and and a
%gdis_end tag. The colour is given in RGB code ranging from 0 to 65k. To look up RGB codes, look e.g. here
http://www.tayloredmktg.com/rgb/.
%gdis_elem
symbol: Na
name: Sodium
number: 11
weight: 22.989799
cova: 0.970000
vdw: 1.450000
charge: 1.000000
colour: 30000 52600 60600
%gdis_end
You can also change the covalent and van der Waal radii here -- these are used to determine bonding so if you have too many or not enough bonds in the molecule, you can fiddle with this.
As an aside, I'm having problems in general with converting .tga and .png to good-looking eps. This is the best I've got so far and uses inkscape. Convert and GIMP don't yield results which are as good.
povray +W400 +H400 $1.pov +A
inkscape --verb FileSave --verb FileClose --export-eps=$1.eps $1.png
Odd though that povray can't directly output vector-based image formats.
Edit: Here are the technical reasons why we're stuck with bitmap formats:
http://news.povray.org/povray.pov4.discussion.general/message/%3C4a79fd58%241%40news.povray.org%3E/#%3C4a79fd58%241%40news.povray.org%3E
24. CCSD mercury /lib/libc.so.6
Mercury is a program for displaying crystal structures from the CCSD.
./mercury
Using native OpenGL
Warning: mercury requires /lib/libc.so.6 but not found
sudo ln -s /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 /lib/libc.so.6
ls /lib/libc.so.6 -lah
/lib/libc.so.6 -> /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6
./mercury
Using native OpenGL
INFO: The environment variable CSDHOME is not set.
You can set CSDHOME by including
export CSDHOME=/home/me/mercury
(use the correct path)
in your ~/.bashrc
25. Daemons...rcconf and update-rc.d
You can easily enable and disable services to load on boot by using rcconf, which is an curses type tool.
Or use sysv-rc-conf:
Alternative, use update-rc.d which doesn't faff around with any gui.
Usage is described
here.
To remove a daemon:
update-rc.d -f apt-cacher-ng remove
To add a daemon:
update-rc.d apt-cacher-ng defaults
If you're more adventurous:
update-rc.d apt-cacher-ng start 20 2 3 4 5 . stop 20 0 1 6 .
where 20 is a two-digit seq code used by init to decide which order to run the script in, and numbers between 1 and 9 and S are the run levels. More information in /etc/inittab
Here: "Default Debian installation does not make any difference between runlevels 2-5. You may customize them to your liking. Runlevels S (single) and 1 are used for maintenance. They start services minimally to avoid possible problems." 0 is halt and 6 is reboot.
26. Adjusting your webcam
I've had problems with webcam images being overly dark -- trying to adjust the image with cheese leads to nothing.
v4l2ucp, which is in the debian repos, however, is a good GUI-based configuration tool which allows you to adjust most things, including, importantly, light sensitivity rather than just brightness.
 |
| v4l2ucp on a much-too-small screen |
27. Command line burning of iso
sudo apt-get install burn
sudo burn -I -n debian.iso
Simple as that.
For burning
audio cds from mp3 files I use a slightly different
approach:
sudo apt-get install brasero-cdrkit mpg123
for i in *.mp3; do mpg123 --rate 44100 --stereo --buffer 3072 --resync -w "`basename "$i" .mp3`".wav "$i"; done
Then name the files in a way that they are listed in desired play order.
ls /dev/cdr
cdrom1 cdrw1
wodim -v -pad speed=1 dev=/dev/cdrw1 -dao -swab *.wav
burns.
28. Finding a file in a package
Two methods:
dpkg --search libglib
apt-file search libglib
(apt-file update before first use)
29. USB support in virtualbox
If you keep getting errors along the lines of:
Failed to access the USB subsystem
and
NS_ERROR_FAILURE
in virtualbox when trying to enable USB devices, make sure that you've added yourself to the vboxusers group in /etc/group. You'll need to reinit before it takes effect (e.g. by rebooting)
30. Startup applications in gnome 3.4
In the past I've always used gnome-session-properties, but it's a hit and miss affair at the moment. So it would be nice with an alternative approach.
According to this:
http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=1992296
anything which is found in /etc/xdg/autostart will be automatically executed, e.g.
cat /etc/xdg/autostart/guake.desktop
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Guake Terminal
Name[pt]=Guake Terminal
Name[pt_BR]=Guake Terminal
Comment=Use the command line in a Quake-like terminal
Comment[pt]=Utilizar a linha de comando em um terminal estilo Quake
Comment[pt_BR]=Utilizar a linha de comando em um terminal estilo Quake
TryExec=guake
Exec=guake
Icon=/usr/share/pixmaps/guake/guake.png
Type=Application
Categories=GNOME;GTK;Utility;TerminalEmulator;
StartupNotify=true
X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=false